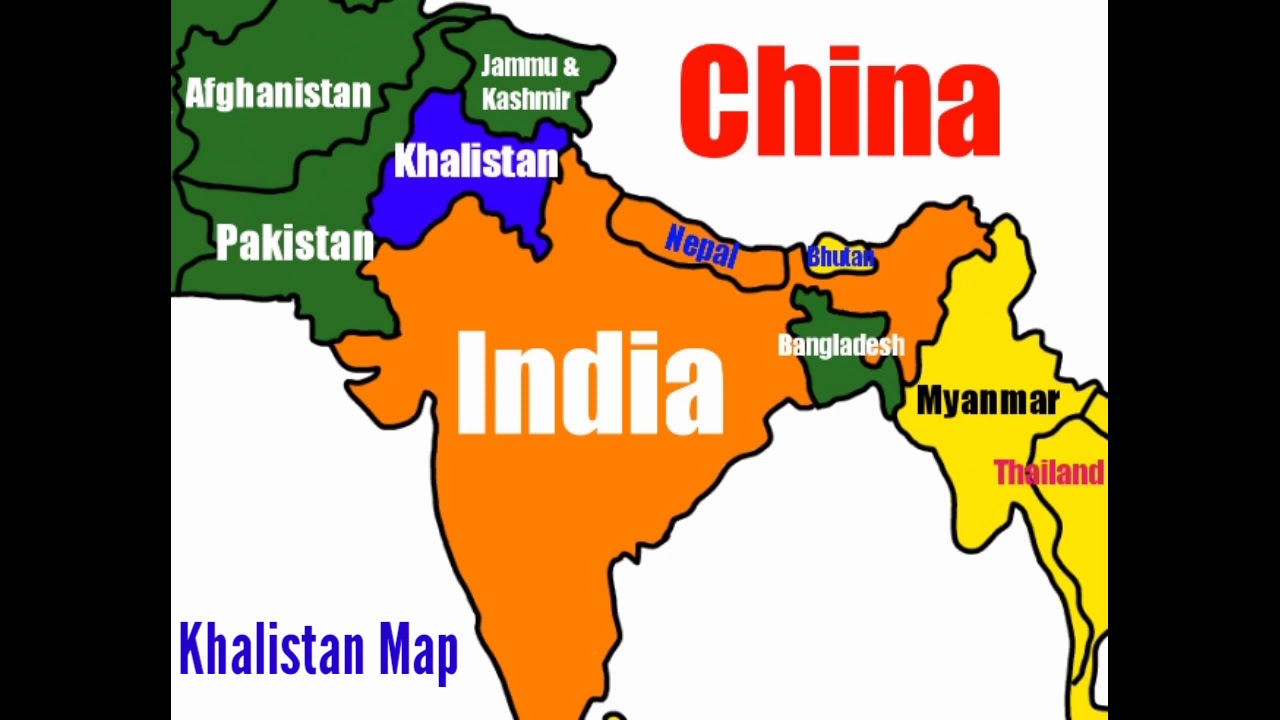
In the vast and intricate tapestry of global geopolitical discourse, few topics have sparked as much debate and controversy as the concept of the Khalistan map. For decades, the notion of an independent Sikh state—Khalistan—has been a potent symbol of aspiration, conflict, and identity for many within the Sikh community, as well as a subject of concern for India and the international community. The Khalistan movement, which seeks to establish a sovereign state in the Punjab region of India, is deeply rooted in historical grievances, cultural identity, and political tensions. Understanding the Khalistan map requires a nuanced exploration of these elements, as well as the political and social dynamics that continue to fuel the movement today.
Tracing the origins of the Khalistan map idea, one must delve into the complex history of the Sikh community in the Indian subcontinent. The historical context is rich with narratives of autonomy, resistance, and the quest for self-determination. The Punjab region, home to a significant Sikh population, has been a focal point of cultural and political struggles, particularly during the partition of India in 1947. The subsequent years saw a series of events that further exacerbated tensions between the Indian state and Sikh leaders, culminating in the demand for Khalistan. This demand is not merely a political statement but is intricately tied to issues of religious identity, economic marginalization, and human rights concerns.
The Khalistan map, however, is not a static or universally agreed-upon concept. It varies widely in interpretation and scope among its proponents, reflecting differing visions of what an independent Sikh state might encompass. For some, it represents a specific geographical area within India’s current borders, while for others, it is a broader cultural and ideological entity that transcends national boundaries. In this article, we will explore the historical background, the motivations behind the Khalistan movement, the various interpretations of the Khalistan map, and the contemporary implications of this ongoing quest for sovereignty.
Table of Contents
- Biography of the Khalistan Movement
- Historical Context of the Khalistan Map
- Cultural and Religious Significance
- Political Motivations and Objectives
- Interpretations of the Khalistan Map
- The Role of Diaspora Communities
- Human Rights and Social Issues
- Impact on Indian Politics
- International Perspectives
- Economic Implications
- Current Developments and Future Prospects
- Media and Public Perception
- Challenges in Defining the Khalistan Map
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
Biography of the Khalistan Movement
The Khalistan movement, a campaign for an independent Sikh state, has its roots deeply embedded in the socio-political fabric of the Indian subcontinent. The movement's origins can be traced back to the early 20th century, but it gained significant traction in the 1970s and 1980s. This period was marked by intense political activity and a series of events that galvanized the Sikh community towards the demand for Khalistan.
The idea of Khalistan emerged against a backdrop of historical grievances and aspirations for self-determination. The Sikh community, with its distinct religious and cultural identity, has historically sought greater autonomy within India. However, the post-independence period witnessed growing discontent among Sikhs, fueled by perceived socio-economic and political marginalization. This discontent was exacerbated by events such as the Green Revolution, which altered the agrarian landscape of Punjab, and the escalating tensions between Sikh leaders and the Indian government.
In the 1980s, the Khalistan movement reached a critical juncture with the emergence of charismatic leaders advocating for a separate Sikh state. The movement was characterized by both peaceful advocacy and violent insurgency, leading to significant political and social upheaval. The Indian government's response to the movement, particularly the military operation at the Golden Temple in 1984, further intensified the demand for Khalistan and led to widespread unrest.
Over the years, the Khalistan movement has evolved, with varying levels of support and activity. While the movement's momentum has waned in India, it continues to find support among Sikh diaspora communities worldwide. These communities play a crucial role in keeping the idea of Khalistan alive, often advocating for the cause through political lobbying, cultural events, and digital platforms.
The Khalistan movement is a complex and multifaceted phenomenon, reflecting the interplay of historical, cultural, and political factors. As we explore the biography of this movement, it is essential to understand the motivations, aspirations, and challenges that have shaped its trajectory over the decades.
Historical Context of the Khalistan Map
The historical context of the Khalistan map is a tapestry woven with threads of cultural identity, colonial legacies, and regional politics. To comprehend the origins of the Khalistan movement and the map that symbolizes it, we must delve into the history of the Sikh community and its relationship with the Indian state.
Sikhism, a religion that emerged in the Punjab region in the 15th century, has always been intertwined with the socio-political dynamics of the area. The Sikhs, known for their martial traditions and a distinct cultural identity, have historically sought to protect their religious freedoms and autonomy. During the British colonial rule, the Punjab region was a significant center of resistance and activism, with Sikhs playing a prominent role in India's struggle for independence.
The partition of India in 1947 was a pivotal moment in the history of the Sikh community. The division of Punjab between India and Pakistan resulted in massive displacement and communal violence, leaving indelible scars on the Sikh psyche. Many Sikhs found themselves on the Indian side of the border, grappling with the challenges of resettlement and integration into a new political order.
In the decades following independence, Sikhs continued to advocate for greater autonomy and recognition of their distinct identity within India. The demand for a Punjabi-speaking state, which culminated in the reorganization of Punjab in 1966, was an early expression of this quest for self-determination. However, the reorganization did not fully address the aspirations of the Sikh community, leading to growing discontent and the eventual emergence of the Khalistan movement.
The Khalistan movement gained momentum in the 1970s, driven by a combination of socio-economic grievances and political factors. The period was marked by escalating tensions between Sikh leaders and the Indian government, culminating in the violent events of the 1980s. The movement's demand for a separate Sikh state was not merely a response to immediate political grievances but was deeply rooted in historical narratives of autonomy and resistance.
The Khalistan map, as envisioned by its proponents, is thus a symbol of this historical quest for self-determination. It represents a geographical space that Sikhs can call their own, free from perceived marginalization and oppression. However, the map is not a static or universally agreed-upon concept, as it reflects diverse interpretations of what an independent Sikh state might encompass.
Cultural and Religious Significance
The Khalistan map is more than just a political aspiration; it carries profound cultural and religious significance for the Sikh community. The quest for Khalistan is deeply intertwined with the Sikh identity, religious tenets, and cultural heritage, making it a potent symbol of self-determination and autonomy.
Sikhism, founded by Guru Nanak in the 15th century, is a monotheistic religion that emphasizes equality, justice, and community service. The religion's teachings are enshrined in the Guru Granth Sahib, the central religious scripture of Sikhism. Over the centuries, Sikhism has evolved as a distinct faith with its own religious practices, cultural traditions, and community institutions.
The Punjab region, considered the heartland of Sikhism, holds immense cultural and religious significance for Sikhs worldwide. It is home to important religious sites, including the Golden Temple in Amritsar, the holiest shrine in Sikhism. The cultural heritage of Punjab, with its vibrant traditions of music, dance, and cuisine, is an integral part of the Sikh identity.
For many Sikhs, the Khalistan map represents a vision of a homeland where their religious and cultural identity can be preserved and nurtured. It is seen as a space where Sikhism can flourish without external interference or marginalization. The demand for Khalistan is thus not just a political statement but a reflection of the community's desire to protect and promote its unique identity.
The cultural and religious significance of the Khalistan map also extends to the Sikh diaspora, who play a crucial role in advocating for the cause. For diaspora communities, the idea of Khalistan is a way to maintain a connection with their ancestral homeland and to assert their cultural identity in a globalized world. Through cultural events, religious congregations, and digital platforms, the diaspora keeps the idea of Khalistan alive, often framing it as a struggle for justice and human rights.
In understanding the cultural and religious significance of the Khalistan map, it is essential to recognize the diverse perspectives within the Sikh community. While some view Khalistan as a necessary step towards preserving their identity, others advocate for greater integration and accommodation within the Indian state. These differing viewpoints reflect the complexity and dynamism of the Sikh community, highlighting the need for dialogue and understanding in addressing the aspirations and concerns of its members.
Political Motivations and Objectives
The political motivations and objectives driving the Khalistan movement are multifaceted, reflecting a complex interplay of historical grievances, socio-economic factors, and aspirations for self-determination. At its core, the movement seeks to establish an independent Sikh state, Khalistan, in the Punjab region of India. However, the motivations behind this demand are not solely political; they are deeply intertwined with cultural, religious, and social dimensions.
One of the primary political motivations of the Khalistan movement is the quest for autonomy and self-governance. Sikhs, with their distinct religious and cultural identity, have historically sought greater political representation and recognition within India. The demand for Khalistan is seen as a way to achieve self-determination, allowing the Sikh community to govern themselves according to their own values and priorities.
The movement is also driven by socio-economic grievances, particularly those related to the agrarian economy of Punjab. Despite being one of India's most prosperous states, Punjab has faced challenges such as declining agricultural productivity, unemployment, and economic disparities. These issues have contributed to a sense of marginalization and disillusionment among the Sikh population, fueling the demand for Khalistan as a solution to their socio-economic woes.
Human rights concerns, particularly those arising from the events of the 1980s, have also played a significant role in shaping the political objectives of the Khalistan movement. The military operation at the Golden Temple in 1984 and the subsequent anti-Sikh riots are seen as watershed moments that highlighted the perceived oppression and discrimination faced by the Sikh community. The demand for Khalistan is framed by its proponents as a struggle for justice and human rights, aimed at addressing historical injustices and ensuring the protection of Sikh identity.
Internationally, the Khalistan movement seeks to garner support from foreign governments and organizations, often framing the demand for an independent Sikh state as a broader issue of minority rights and self-determination. Sikh diaspora communities play a crucial role in this endeavor, leveraging their political influence and networks to advocate for the cause on the global stage.
While the political motivations and objectives of the Khalistan movement are diverse, they are united by a common aspiration for autonomy and self-determination. The movement reflects the complex and dynamic nature of Sikh identity and politics, highlighting the need for dialogue and engagement in addressing the aspirations and concerns of the Sikh community.
Interpretations of the Khalistan Map
The Khalistan map is a concept that has been subject to various interpretations and visions, reflecting the diverse aspirations and perspectives within the Sikh community. While the overarching goal of the Khalistan movement is to establish an independent Sikh state, the specifics of what this state would entail, including its geographical boundaries and governance structure, vary widely among its proponents.
One interpretation of the Khalistan map envisions a state within the current geographical boundaries of the Indian Punjab. This vision focuses on the areas with a significant Sikh population, emphasizing the cultural and historical ties of Sikhs to the Punjab region. Proponents of this interpretation argue that an independent Punjab would allow Sikhs to exercise self-governance and protect their religious and cultural identity.
Another interpretation of the Khalistan map is more expansive, envisioning a broader territory that includes parts of neighboring states with historical and cultural significance to Sikhs. This vision is rooted in the historical context of the Sikh Empire in the 19th century, which extended beyond the present-day boundaries of Punjab. Proponents of this interpretation argue for a Khalistan that encompasses regions historically ruled by Sikh leaders, reflecting a more expansive view of Sikh sovereignty.
Some proponents of the Khalistan movement also advocate for a transnational or ideological interpretation of the Khalistan map. In this view, Khalistan is not limited to a specific geographical territory but represents a broader cultural and ideological space for Sikhs worldwide. This interpretation emphasizes the global Sikh identity and the importance of preserving Sikh culture and values in the diaspora.
The differing interpretations of the Khalistan map highlight the complexity and diversity of the movement. They reflect the varying priorities and aspirations of Sikhs, both within India and in the diaspora. While some view Khalistan as a necessary step towards preserving Sikh identity and autonomy, others advocate for greater integration and accommodation within the Indian state.
The challenge in defining the Khalistan map lies in balancing these diverse perspectives and aspirations. It requires a nuanced understanding of the historical, cultural, and political factors that have shaped the movement and a willingness to engage in dialogue and negotiation to address the concerns of all stakeholders involved.
The Role of Diaspora Communities
Diaspora communities play a crucial role in the Khalistan movement, providing support, resources, and advocacy for the cause on the global stage. These communities, spread across countries such as Canada, the United States, the United Kingdom, and Australia, have been instrumental in keeping the idea of Khalistan alive and advocating for Sikh rights and self-determination.
The Sikh diaspora's involvement in the Khalistan movement is driven by a strong sense of cultural and religious identity, as well as a desire to maintain a connection with their ancestral homeland. For many diaspora Sikhs, the Khalistan map represents a vision of a homeland where their cultural and religious identity can be preserved and nurtured. This vision is often framed as a struggle for justice and human rights, resonating with broader issues of minority rights and self-determination.
Diaspora communities leverage their political influence and networks to advocate for the Khalistan cause in their host countries. Through political lobbying, cultural events, and digital platforms, they raise awareness about the movement and seek to garner support from foreign governments and organizations. The diaspora's advocacy efforts often focus on issues such as human rights violations, cultural preservation, and the right to self-determination for Sikhs.
In addition to advocacy, diaspora communities also play a significant role in providing financial and logistical support for the Khalistan movement. Fundraising efforts, cultural events, and community organizations are mobilized to support the cause, both within India and internationally. This support is vital for sustaining the movement and keeping the idea of Khalistan alive in the global consciousness.
The involvement of diaspora communities in the Khalistan movement is not without its challenges. Differences in perspectives and priorities between diaspora and local Sikhs can create tensions and complexities in advancing the movement's objectives. Additionally, the geopolitical dynamics of host countries and their relationships with India can impact the diaspora's advocacy efforts.
Despite these challenges, diaspora communities remain a vital force in the Khalistan movement, providing a global platform for advocacy and support. Their involvement underscores the transnational nature of the movement and the importance of engaging with diverse perspectives and stakeholders in addressing the aspirations and concerns of the Sikh community.
Human Rights and Social Issues
The Khalistan movement is deeply intertwined with human rights and social issues, reflecting the complex interplay of historical grievances, socio-economic challenges, and aspirations for justice and equality. At its core, the movement seeks to address perceived oppression and discrimination faced by the Sikh community, both within India and in the diaspora.
One of the central human rights concerns driving the Khalistan movement is the legacy of the 1984 anti-Sikh riots and the military operation at the Golden Temple. These events are seen as watershed moments that highlighted the perceived marginalization and victimization of Sikhs by the Indian state. The movement's demand for Khalistan is framed as a struggle for justice and accountability for these historical injustices, as well as a means of ensuring the protection of Sikh identity and religious freedoms.
Socio-economic issues, particularly those related to the agrarian economy of Punjab, also play a significant role in shaping the movement's objectives. Despite being one of India's most prosperous states, Punjab faces challenges such as declining agricultural productivity, unemployment, and economic disparities. These issues contribute to a sense of marginalization and disillusionment among the Sikh population, fueling the demand for Khalistan as a solution to their socio-economic woes.
The Khalistan movement also raises broader issues of minority rights and self-determination, resonating with global conversations on these topics. Proponents of the movement argue for the right of Sikhs to establish an independent state where their cultural and religious identity can be preserved and nurtured. This demand is often framed as part of a broader struggle for justice and equality for minority communities worldwide.
The movement's focus on human rights and social issues underscores the importance of addressing the underlying grievances and aspirations of the Sikh community. It highlights the need for dialogue and engagement in addressing these concerns and finding solutions that respect the rights and aspirations of all stakeholders involved.
Impact on Indian Politics
The Khalistan movement has had a significant impact on Indian politics, shaping the political landscape of Punjab and influencing broader national conversations on autonomy, minority rights, and federalism. The movement's demand for an independent Sikh state has been a source of tension and conflict, affecting the dynamics between the Indian state and the Sikh community.
In Punjab, the Khalistan movement has played a central role in shaping the state's political landscape. The movement's influence is reflected in the rise of regional political parties and leaders advocating for greater autonomy and recognition of Sikh identity. Over the years, the movement has led to shifts in political alliances and electoral outcomes, as parties seek to address the aspirations and concerns of the Sikh population.
At the national level, the Khalistan movement has raised broader questions about the nature of Indian federalism and the rights of minority communities. The movement's demand for Khalistan is seen as part of a broader conversation on the distribution of power and resources between the central government and states. It has also prompted discussions on the need for greater accommodation and integration of diverse cultural and religious identities within the Indian state.
The movement's impact on Indian politics is not limited to electoral dynamics and policy debates. It has also influenced the broader discourse on nationalism and identity, challenging dominant narratives and highlighting the complexities of India's multicultural society. The movement's emphasis on justice and human rights resonates with broader societal conversations on these issues, contributing to a more nuanced understanding of the challenges facing minority communities in India.
The Khalistan movement's impact on Indian politics underscores the need for dialogue and engagement in addressing the aspirations and concerns of the Sikh community. It highlights the importance of finding solutions that respect the rights and aspirations of all stakeholders involved, while also promoting unity and cohesion within India's diverse society.
International Perspectives
The Khalistan movement is not confined to the borders of India; it has garnered international attention and support, influencing global conversations on minority rights, self-determination, and human rights. The movement's transnational nature is reflected in the involvement of Sikh diaspora communities and the advocacy efforts of international organizations and governments.
Internationally, the Khalistan movement resonates with broader issues of minority rights and self-determination, aligning with global conversations on these topics. Proponents of the movement argue for the right of Sikhs to establish an independent state where their cultural and religious identity can be preserved and nurtured. This demand is often framed as part of a broader struggle for justice and equality for minority communities worldwide.
Sikh diaspora communities play a crucial role in advocating for the Khalistan cause on the global stage. Through political lobbying, cultural events, and digital platforms, they raise awareness about the movement and seek to garner support from foreign governments and organizations. The diaspora's advocacy efforts often focus on issues such as human rights violations, cultural preservation, and the right to self-determination for Sikhs.
The involvement of international organizations and governments in the Khalistan movement is shaped by a complex interplay of geopolitical dynamics and diplomatic considerations. While some countries and organizations have expressed support for the movement's human rights and minority rights agenda, others have been cautious in their engagement, taking into account their relationships with India and broader regional considerations.
The international perspectives on the Khalistan movement highlight the importance of dialogue and engagement in addressing the aspirations and concerns of the Sikh community. They underscore the need for a nuanced understanding of the movement's objectives and the broader geopolitical dynamics shaping its trajectory.
Economic Implications
The Khalistan movement has significant economic implications, both for the Punjab region and for India as a whole. The movement's demand for an independent Sikh state raises questions about the distribution of resources, economic development, and trade relations, highlighting the complex interplay between politics and economics.
In Punjab, the Khalistan movement is driven by socio-economic grievances, particularly those related to the agrarian economy. Despite being one of India's most prosperous states, Punjab faces challenges such as declining agricultural productivity, unemployment, and economic disparities. These issues have contributed to a sense of marginalization and disillusionment among the Sikh population, fueling the demand for Khalistan as a solution to their socio-economic woes.
The demand for Khalistan also raises questions about the distribution of resources and economic development in the region. Proponents of the movement argue that an independent Sikh state would allow for more effective governance and resource allocation, addressing the socio-economic challenges facing Punjab and promoting sustainable development.
On a broader scale, the Khalistan movement has implications for India's economy and trade relations. The movement's demand for an independent state raises questions about the impact on trade and economic cooperation between India and its neighbors, as well as the potential for increased regional instability and conflict.
The economic implications of the Khalistan movement underscore the importance of addressing the underlying grievances and aspirations of the Sikh community. They highlight the need for dialogue and engagement in finding solutions that promote economic development and prosperity for all stakeholders involved.
Current Developments and Future Prospects
The Khalistan movement, while not as active as it was in the 1980s, continues to be a relevant and evolving issue. Current developments and future prospects of the movement are shaped by a combination of political, social, and economic factors, reflecting the complex dynamics of Sikh identity and aspirations.
In recent years, the Khalistan movement has seen a resurgence of interest, particularly among Sikh diaspora communities. This renewed interest is driven by a combination of cultural preservation efforts, advocacy for minority rights, and a desire to address historical grievances. Digital platforms and social media have played a significant role in mobilizing support for the movement, providing a global platform for advocacy and dialogue.
Within India, the Khalistan movement remains a sensitive and contentious issue, influencing political dynamics and policy debates. The movement's demand for greater autonomy and recognition of Sikh identity continues to shape the political landscape of Punjab, with regional parties and leaders advocating for the aspirations and concerns of the Sikh community.
Future prospects for the Khalistan movement are shaped by a combination of domestic and international factors. Domestically, the movement's trajectory will depend on the Indian government's response to Sikh grievances and aspirations, as well as the broader socio-economic and political dynamics within Punjab. Internationally, the movement's future will be influenced by the involvement of diaspora communities and the geopolitical dynamics of the region.
While the Khalistan movement faces significant challenges, it remains a relevant and evolving issue, reflecting the complex dynamics of Sikh identity and aspirations. The movement's future prospects highlight the importance of dialogue and engagement in addressing the aspirations and concerns of the Sikh community, as well as the broader challenges facing minority communities in India and beyond.
Media and Public Perception
The media and public perception of the Khalistan movement play a significant role in shaping the discourse and understanding of the movement's objectives and implications. The portrayal of the Khalistan movement in the media, both in India and internationally, influences public opinion and policy debates, highlighting the complexities and sensitivities of the issue.
In India, the media's portrayal of the Khalistan movement has been shaped by a combination of historical narratives, political dynamics, and security concerns. The movement is often framed in terms of its historical roots, highlighting the socio-political and cultural factors that have driven the demand for Khalistan. Media coverage also emphasizes the security implications of the movement, focusing on issues such as insurgency, terrorism, and regional stability.
Internationally, the media's portrayal of the Khalistan movement is influenced by broader conversations on minority rights, self-determination, and human rights. The movement is often framed as part of a global struggle for justice and equality, resonating with broader issues of minority rights and self-determination. The involvement of Sikh diaspora communities in advocating for the Khalistan cause is also highlighted, reflecting the transnational nature of the movement.
Public perception of the Khalistan movement is shaped by a combination of media narratives, historical context, and personal experiences. For many Sikhs, the movement represents a quest for justice, autonomy, and cultural preservation, reflecting the community's aspirations and grievances. For others, the movement is associated with issues of insurgency and security, highlighting the complexities and sensitivities of the issue.
The media and public perception of the Khalistan movement highlight the importance of dialogue and engagement in addressing the aspirations and concerns of the Sikh community. They underscore the need for a nuanced understanding of the movement's objectives and implications, as well as the broader challenges facing minority communities in India and beyond.
Challenges in Defining the Khalistan Map
Defining the Khalistan map presents several challenges, reflecting the diverse perspectives and aspirations within the Sikh community, as well as the complex historical and political context of the movement. The varying interpretations of the Khalistan map highlight the complexities and sensitivities of the issue, underscoring the need for dialogue and engagement in addressing the aspirations and concerns of all stakeholders involved.
One of the primary challenges in defining the Khalistan map is reconciling the diverse interpretations and visions of what an independent Sikh state might encompass. While some proponents envision a state within the current geographical boundaries of the Indian Punjab, others advocate for a more expansive territory that includes parts of neighboring states with historical and cultural significance to Sikhs. These differing interpretations reflect the varying priorities and aspirations of Sikh communities, both within India and in the diaspora.
The challenge of defining the Khalistan map is further complicated by the complex historical and political context of the movement. The demand for Khalistan is deeply rooted in historical grievances and aspirations for self-determination, but it also intersects with broader issues of regional stability, economic development, and minority rights. Balancing these diverse factors and finding a solution that respects the rights and aspirations of all stakeholders is a complex and sensitive task.
The geopolitical dynamics of the region also present challenges in defining the Khalistan map. The movement's demand for an independent Sikh state has implications for India's territorial integrity and regional stability, influencing the broader geopolitical landscape of South Asia. Finding a solution that addresses the aspirations of the Sikh community while ensuring regional stability and security is a complex and multifaceted challenge.
The challenges in defining the Khalistan map highlight the importance of dialogue and engagement in addressing the aspirations and concerns of the Sikh community. They underscore the need for a nuanced understanding of the movement's objectives and implications, as well as the broader challenges facing minority communities in India and beyond.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the Khalistan map?
The Khalistan map represents the vision of an independent Sikh state, Khalistan, primarily in the Punjab region of India. The map encompasses varying interpretations and visions of what this state might entail, reflecting the diverse aspirations and perspectives within the Sikh community.
2. Why do some Sikhs support the Khalistan movement?
Some Sikhs support the Khalistan movement due to historical grievances, socio-economic challenges, and aspirations for self-determination. The movement is seen as a way to achieve autonomy and preserve Sikh cultural and religious identity, addressing perceived marginalization and oppression.
3. What role do diaspora communities play in the Khalistan movement?
Diaspora communities play a crucial role in the Khalistan movement by providing support, resources, and advocacy for the cause on the global stage. Through political lobbying, cultural events, and digital platforms, they raise awareness about the movement and seek to garner support for Sikh rights and self-determination.
4. How has the Khalistan movement impacted Indian politics?
The Khalistan movement has significantly impacted Indian politics by shaping the political landscape of Punjab and influencing broader national conversations on autonomy, minority rights, and federalism. The movement's demand for an independent Sikh state has been a source of tension and conflict, affecting the dynamics between the Indian state and the Sikh community.
5. What are the economic implications of the Khalistan movement?
The Khalistan movement has significant economic implications, particularly for the Punjab region and India as a whole. The movement raises questions about the distribution of resources, economic development, and trade relations, highlighting the complex interplay between politics and economics.
6. What are the challenges in defining the Khalistan map?
Defining the Khalistan map presents several challenges, including reconciling diverse interpretations and visions of what an independent Sikh state might encompass, balancing historical grievances with contemporary political and economic realities, and addressing regional stability and security concerns.
Conclusion
The Khalistan map is a complex and multifaceted symbol of the Sikh community's quest for self-determination, identity, and justice. Understanding the Khalistan movement requires a nuanced exploration of its historical roots, cultural significance, political motivations, and diverse interpretations. The movement reflects the aspirations and grievances of a community striving for autonomy and recognition, while also highlighting broader issues of minority rights and self-determination.
The Khalistan movement's impact is felt not only in the Punjab region but also in the broader Indian political landscape and international discourse. The involvement of Sikh diaspora communities and the transnational nature of the movement underscore its significance as a global conversation on justice, equality, and cultural preservation.
Addressing the aspirations and concerns of the Sikh community requires dialogue, engagement, and a willingness to find solutions that respect the rights and aspirations of all stakeholders involved. The challenges in defining the Khalistan map and navigating the complex dynamics of the movement highlight the importance of understanding the diverse perspectives and historical context that have shaped its trajectory.
As the Khalistan movement continues to evolve, it remains a relevant and dynamic issue, reflecting the complexities of Sikh identity and the broader challenges facing minority communities in India and beyond. The movement's future prospects will depend on the ability of all stakeholders to engage in meaningful dialogue and collaboration, fostering a more inclusive and harmonious society for all.